How to Use AI to Generate SQL Queries

AI-powered tools like ChatGPT, Claude, and other Large Language Models (LLMs) have made generating SQL queries much easier. These tools can translate natural language requests into SQL code, making database querying more accessible, even for non-technical users. This post will guide you on how to use AI as an SQL query generator and enhance your data analysis capabilities.
Why Use AI SQL Generators?
Leveraging an AI SQL generator has several benefits:
- Simplifies complex SQL tasks: You no longer need to write queries from scratch.
- Saves time: AI tools can create queries much faster than manual coding.
- Reduces errors: AI can produce correct SQL syntax, reducing human mistakes.
- Accessible to non-developers: Users with minimal SQL knowledge can still work effectively with databases.
Using AI for SQL Query Generation: Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Retrieve Your Database Schema
To effectively generate SQL queries, the AI needs to understand the structure of your database (tables, columns, and relationships). You can provide the schema as context by first querying your database for its structure.
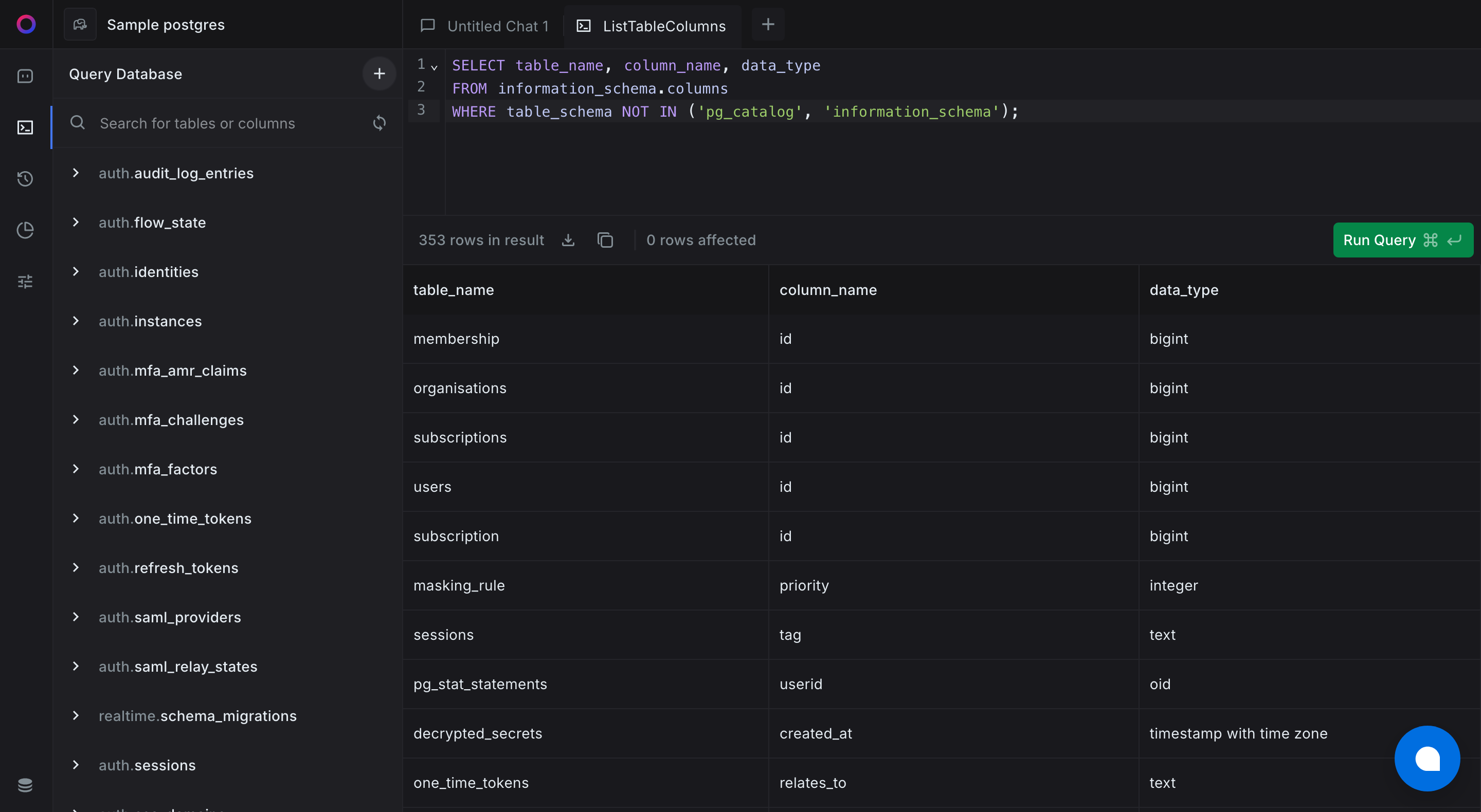
Here’s a PostgreSQL query to retrieve all user-defined tables and columns, ignoring default system tables:
SELECT table_name, column_name, data_type
FROM information_schema.columns
WHERE table_schema NOT IN ('pg_catalog', 'information_schema');
 Tip: You can use Sequel to connect your database and execute queries
Tip: You can use Sequel to connect your database and execute queries
This query fetches the names of all user-defined tables and their columns, excluding PostgreSQL’s system tables.
Step 2: Craft a System Prompt for the AI
Next, you need to craft a clear and informative system prompt to inject into the AI (like ChatGPT or Claude). This helps the AI understand the database and business context, enabling it to generate precise SQL queries.
Here’s an optimized system prompt you can use:
System Prompt:
You are an expert SQL assistant helping analyze a retail company's sales and product database. The following schema describes the database structure:
- Tables:
- customers:
id(integer),name(text),email(text),signup_date(date) - orders:
id(integer),customer_id(integer),order_date(date),total_amount(decimal) - products:
id(integer),name(text),category(text),price(decimal) - order_items:
id(integer),order_id(integer),product_id(integer),quantity(integer)
- customers:
Use this schema to generate SQL queries when I ask questions about customer orders, product sales, and other business data.
Step 3: Ask AI for SQL Queries
With the schema in place, you can now ask specific questions, and the AI will generate SQL queries accordingly. For instance:
Example Question:
"Show me all orders placed in the last 30 days with a total amount greater than $100."
AI-Generated SQL Query:
SELECT *
FROM orders
WHERE order_date >= NOW() - INTERVAL '30 days'
AND total_amount > 100;
This query retrieves all orders from the past 30 days with a total amount exceeding $100.
Here are more examples for Step 3 to help users generate SQL queries using AI:
Example 2: Retrieve Total Sales by Product
"Show me the total sales for each product."
AI-Generated SQL Query:
SELECT p.name, SUM(oi.quantity * p.price) AS total_sales
FROM order_items oi
JOIN products p ON oi.product_id = p.id
GROUP BY p.name;
This query calculates the total sales for each product by multiplying the quantity of each order item by the product price.
Example 3: Find Customers with Orders Over $500
"List customers who have placed orders over $500."
AI-Generated SQL Query:
SELECT c.name, c.email, o.total_amount
FROM customers c
JOIN orders o ON c.id = o.customer_id
WHERE o.total_amount > 500;
This query retrieves customers who placed orders with a total amount exceeding $500.
Example 4: Orders by Category
"Show me the total orders by product category."
AI-Generated SQL Query:
SELECT p.category, COUNT(*) AS total_orders
FROM order_items oi
JOIN products p ON oi.product_id = p.id
GROUP BY p.category;
This query groups the total number of orders by product category.
Step 4: Review and Execute Queries
After AI generates the SQL query, review it for accuracy and then run it in your database.
How Sequel Enhances SQL Query Generation
Sequel offers several powerful features that simplify the SQL querying process:
- No Manual Schema Uploads: Automatically connects to your database, eliminating the need for manual schema dumps.
- Instant Query Execution: Queries are run immediately, and results are returned without extra steps.
- Error Correction: Automatically fixes SQL errors for a smoother experience.
- Data Visualization: Generates charts and graphs from query results for easier data analysis.
With these features, Sequel saves time and boosts productivity, making it an ideal solution for data teams.
Conclusion
Using AI SQL generators like ChatGPT, Claude, or specialized tools allows you to interact with databases effortlessly. By providing a schema and crafting system prompts, you can quickly generate accurate SQL queries for data retrieval, analysis, and business insights.
Start exploring your data with Sequel
Save hours of time writing SQL queries. Get started for free.
